英语句子基本句型有趣课件_英语基本句型及例句教案
1.一个英语句子中各个成分的位置是怎么放的?
2.英语 7种 基本句型
3.英语中简单句的五种基本句型
4.英语中的五大句型
5.高中英语五种基本句型及拓展
6.英语5个基本句型例句
7.用英语的五种基本句型造各造5个句子
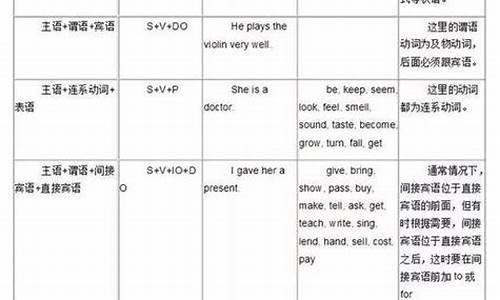
英语基本句型讲解:
英语句子成分的排列顺序与汉语不同。汉语放在前面的,英语可能要放在后面;而汉语放后面的,英语可能放在前面。即使是同样一句话,如果用词不同,句中的次序也会有变化。
英语五种基本句型列式:
1、主+谓
2、主+系+表
3、主+谓+宾
4、主+谓+间宾+直宾
5、主+谓+宾+宾补
扩展资料
第一种 主语 + 谓语动词 + 表语(S+V+P)
The bike is new.
The map is on the wall.
第二种 主语+不及物动词 (S+V)
He swims.
第三种 主语+及物动词+宾语 (S+V+O)
Children often sing this song.
第四种 主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语 (S+V+IO+DO)
She showed her friends all her pictures.
第五种 主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语 (S+V+O+C)
1. 主语+谓语(不及物动词) [S + V]
如:The children are playing hily.
孩子们正在高兴地玩。
2. 主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语 [S+V+O]
如:The Greens enjoy living in China.
格林一家喜欢住在中国。
3. 主语+谓语+表语 [S+V+P]
该句型谓语动词为连系动词。常见的系动词有:be(是); get(变得), become(成为), turn(变得), look(看起来), feel(感到), smell(闻起来), taste(尝起来), sound(听起来), seem(似乎) 等。如:
① He became a famous doctor.
他成为了一名著名的医生。
② The le pie tastes really delicious.
苹果派吃起来真是好吃。
4. 主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语 [S+V+InO+DO]
这种句型中的及物动词后跟双宾语,既指人的间接宾语和指物的直接宾语。也可以把间接宾语放在直接宾语之后,但要加介词for或to。如:
① My aunt bought me a computer. = My aunt bought a computer for me. 我阿姨买给我一台电脑。
② I passed him the salt. = I passed the salt to him.
我把盐递给他。
5. 主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语 [S+V+O+OC]
如:We must keep our school clean.
我们必须保持我们的学校清洁。
1. Subject (主语) + Verb (谓语)
这种句型中的动词大多是不及物动词,这些动词常见的有:ear, apologize,arrive, come, die, disear, exist, fall, hen, rise,等等。如:
The students work very hard.学生们学习很努力。
She apologized to me again. 她再次向我道歉。
The accident hened yesterday evening.事故是昨天晚上发生的。
2. Subject (主语) + Link. V(系动词) + Predicate(表语)
这种句型中的系动词一般可分为下列两类:
(1)表示状态的连系动词。这些词有:be, look, seem, ear, smell, taste, sound, keep, remain, 等等。如:
Several players lay flat on the playground.
几个队员平躺在操场上。
We should remain modest and prudent any time.
我们在任何时候都应该保持谦虚谨慎。
This kind of food tastes terrible.
这种食物吃起来很糟糕。
The picture looks more beautiful at a certain distance.
这幅画在一定的距离看更漂亮一些。
(2)表示转变或结果的系动词。这些词有:become, get, grow, turn, go, come, prove,等等。如:
Spring comes. It is getting warmer and warmer.春天到了,天气变得越来越暖和。
Don't he the food. It has gone bad.不要吃那种食物,已经变质了。
The facts prove true.事实证明是正确的。
3. Subject(主语) + Verb (谓语) + Object (宾语)
这种句型中的动词应为及物动词或者可以后接宾语的动词短语。同时,句子中有时含有与宾语有关的状语。作宾语的成分常是:名词、代词、动词不定式、动名词或从句。如:
You can put the books in your bag.
你可以把书放在书包里。
Farmers in our area grow lots of vegetables.
我们这里的.农民种很多种蔬菜。
She lost the chance to make her earance on the stage.
她失去了在舞台上露面的机会。
I prefer to make web pages.我更喜欢做网页。
4. Subject(主语)+Verb(谓语)+ Indirect object(间接宾语)+Direct object (直接宾语)
这种句型中作间接宾语的常常指“人”,直接宾语常常指“物”。如:
Yesterday her father bought her a bicycle as a birthday present.
昨天她父亲给她买了一辆自行车作为生日礼物。
The old man is telling the children stories in the Long March.
老人正在给孩子们讲长征中的故事。
这种句型还可转换为其他两种句型:
1)动词 + 宾语 + for sb.;
2)动词 + 宾语+to sb.。如:
Please show me your picture.
= Please show your picture to me.
请把你的画给我看一下。
I'll offer you a good chance as long as you don t lose heart.
= I'll offer a good chance for you as long as you don't lose heart.
只要你不失去信心,我会给你提供机会的。
5. Subject(主语)+Verb (动词)+Object (宾语)+Complement(补语)
这种句型中的宾语+ 补语可统称为“复合宾语”。担任补语的常常是名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、分词、动词不定式等。如:
Keep the children quiet, please. 请让孩子们安静下来。
He painted the wall white. 他把墙漆成白色。
We found him an honest person.我们发现他是一个诚实的人。
His mother told him not to play on the street.他母亲告诉他不要在街上玩。
注意:动词he, make, let, see, hear, notice, feel, observe, watch等后面所接的动词不定式作宾补时,不带to。如:
The boss made him do the work all day.老板让他整天做那项工作。
一个英语句子中各个成分的位置是怎么放的?
一、以形式主语it引导的句型。
句型1. It hened(chanced) that +clause. = sb. hened /chanced sth. = sb. did sth. by chance. 如:
It hened that he was out when I got there. 当我到那儿时,碰巧他不在。=He hened to be out when I got there.= It chanced that he was out when I got there= He was out by chance when I got there.
句型2、It seems that sb. do/ be doing/ he done/ had done= Sb. seems to do/ be doing/ he done/ had done 如:(还有动词ear可这样使用)
It seemed that he had been to Beijing before.好象你以去过北京。=He seemed to he been Beijing before.
句型3. It is / was+被强调的部分+that(who)+剩余的部分.如:
It wasn’t until he came back that I went to bed.直到他回来我才睡觉。(一定要注意被强调句型谓语动词否定的转移,及形式)。
It was because he was ill that he didn’t come to school today.只因为他有病了今天没有来上学。(只能用because而不能用for, as 或since)
It is I who am a student. 我确实是个学生。(句中am不能用are来代替。)
句型4、It is high time (time/ about time) (that) 主语+should do / did+其它。(注意从句中的谓语动词用的是虚拟语气)
It is high time that we should go / went home.我们该回家了。
句型5、It is / was said ( reported…)+that+从句. 如:
It was said that he had read this novel.据说他读过这篇。=He was said to he read this novel.
句型6、It is impossible / necessary/ strange…that clause.(从句中的谓语用should+do / should he done,其形式是虚拟语气。)如:
It is strange that he should he failed in this exam.真奇怪,他这次考试没有及格。
句型7、It is + a pity/ a shame…that clause.(注意从句中的谓语动词用should do或should he
done的形式,但should可以省略。)如:
He didn’t come back until the film ended. It was a pity that he should he missed this film. 他直到**结束才回来。他没有看到这部**真可惜。
句型8、It is suggested / ordered/ commanded /…that +clause.(从句的谓语动词用should do, 但should可以省略。)如:
It is suggested that the meeting should be put off.有人建议推迟会议。
句型9、It is/was+表示地点的名词+where+从句。(注意本句不是强调句型,而是以where引导的定语从句。)如:
It was this house where I was born.请比较:It was in this house that I was born. (后一句是强调句型。)
句型10、It is / was +表示时间的名词+when+从句。(注意本句型也不是强调句型,而是以when引导的定语从句。)如:
It was 1999 when he came back from the United States. 请比较:It was in 1999 that he came back from the United States.
句型11、It is well-known that+从句。如:
It is well-known that she is a learned woman. 众所周知,她是个知识渊博的妇女。
句型12、It is +段时间+since+主语+did. 请比较:
It was +段时间+since+主语+had done. 如:
It is five years since he left here.他已经离开这儿五年了。
It was five years since he left here.(同上)
句型13、It +谓语+段时间+before+主语+谓语.( before引导的是时间状语从句。) 如:
It wasn’t long before the people in that country rose up.没有多久那个国家的人民就起义了。
It will be three hours before he comes back.三个小时之后他才能回来。
句型14、It is +形容词+for+ sb.+ to do. 如:
It is impossible for me to finish this work before tomorrow.我明天之前完成此工作是不可能的。
句型15、It is +(心理品质方面的)形容词+of + sb. + to do. = 主语+ be +形容词+to do.(常用的形容词有:kind, stupid; foolish, good, wise等。)如:
It is kind of you to help me.=You are kind to help me.你真好给我提供了帮助。
二、定语从句:
句型16、由as引导的非限定性的定语从句。如:
As we he known, he is a most good student.众所周知,他是个很好的学生。请比较:It is well-known that he is a most good student.(前一个是定语从句,而后者是个主语从句。)
句型17、由which引导的非限定性的定语从句。如:
He is a professor, which I he been looking forward to becoming.
他是个教授,那是我一直盼望的职业。(因为先行词professor是表示职业的名词,因此引导词用which,而不用who。(注意:关于which和as之间的比较请看语法的定语从句部分。)
句型18、由where, when引导的定语从句(其中包括限定性的或非限定性的。)如:
This is the house where I used to come.请比较:This is the house which / that I used to come to.
This is the day when I joined the Party.请比较:This is the day which / that I joined the Party on.
说明:关于that与which之间的区别,请看语法中的定语从句。
三、让步状语从句
句型19、No matter what / which / who / where / when /
whose+从句,+主句。注意从句中的时态一般情况用一般现在时态。如:
No matter what you do, you must do it well.请比较:Whatever you do, you must do it well. 无论你做什么,一定要做好。
No matter where you go, please let me know.请比较:Wherever you go, please let me know.你无论去哪儿,请通知我。
说明:这两种句型形式不同,而意义完全相同。
注意:I will tell whoever would like to read it.
句中的whoever不能用whomever来代替。因为它即作动词tell的宾语,又作后面从句的主语。
四、条件状语从句
句型20、When / So long as / As long as / Once +从句,+主句。(从句也可以放在主句之后。)如:
As long as you give me some money, I will let you go.只要你给我一些钱,我就让你走。
Once you he begun to learn English, you should learn it well.
一旦你开始学习英语,你应该把它学好。
句型21、主句+on condition that+从句。如:
I will go with you on condition that you give me some money.我和你一起去的条件是你给我一些钱。
句型22、主句+unless+从句.(注意:由于unless本身是否定词,所引导的从句的谓语动词用肯定。)如:
I will go there tomorrow unless it rains.我明天去那儿除非下雨。
句型23、祈使句,+and/ and then+主句。(注意:祈使句也可用一个名词短语。)如:
Use your head, and you will find a good idea.动脑筋想一想,你就会想出一个好主意。
Another word, and I will beat you.你再说一句,我就揍你。
句型24、If +necessary / impossible/ important等,+主句。如:
If necessary, I will do it. 如果有必要的话,我来做此事。
五、原因状语从句
句型25、主句+in case+从句。(in case表示以免)如:
I will take my raincoat in case it rains.我要把雨衣带上以免下雨。
句型26、主句+due to / because of / owning to / + the fact that +从句。如:
He did not come to school because of the fact that he was
ill.由于他有病了,所以没有来上学。
六、时间状语从句
句型27、When / While / As +从句,+主句。(关于它们之间的区别请看语法。)如:
When I was in the country, I used to carry some water for you.当我在农村时,我常常给你打水。
句型28、主句+after / before +从句. 如:
They hadn’t been married four months before they were
devoiced.他们绘结婚不到四个月就离婚了。
We went home after we had finished the work.我们做完此工作就回家了。
句型29、主语+肯定谓语+until+从句(或时间).请比较:
主语+否定谓语+until+从句。如:
I worked until he came back.我一直工作到他回来。
I didn’t worked until he came back.他回来我才开始工作。
句型30、As soon as / Immediately / Directly / Instantly / The moment / The instant / The minute +从句,+主句. 如:
My father went out immediately I got home.我一到家,我父亲就出去了。
句型31、No sooner +had + 主语+done…than +主语+did. 请比较:
主语+had + no sooner +done…than +主语+did. 如:
No sooner had I got to Beijing than I called you.我一到北京就给你打电话了。
I had no sooner got to Beijing than I called you.
句型32、Hardly +had +主语+done…when / before + 主语+did.请比较:主语+had +hardly +
done…when / before +主语+did.
Hardly had she had supper when she went out. 她一吃完晚饭就出去了。
She had hardly had supper when she went out.
句型33、By the time+从句,+主句.(注意时态的变化。)如:
By the time you came back, I had finished this book.到你回来时,我已经写完了这本书。
By the time you come back, I will he finished this book.到你回来时,我将写完这本书。
句型34、each / every time +从句,+主句. (这时相当于whenever 或no matter
when引导的从句。从句也可放在主句之后。)如:
Each time he comes to Harbin, he always drops in on me.每当他来哈尔滨,总是随便来看看我。
七、地点状语从句
句型35、Where +从句,+主句. 如:
Where there is no rain, farming is difficult or impossible.哪里没有雨水,种庄稼是很难的或者是不可能的。
句型36、Anywhere / wherever+从句,+主句. 如:
Anywhere I go, my wife goes too.无论我去哪儿,我的妻子也去哪儿。
I will go wherever you suggest.你建议我去哪儿,我就去哪儿。
八、目的状语从句
句型37、主句+in order that / so that +从句.如:
I got up early in order that I could catch the first bus.我起得很早,以便能赶上早班车。
句型38、主句+for + sb. +to do.(注意动词不定式复合结构在这儿作目的状语。)如:
He came here for me to work out this problem.他来这儿叫我帮他解出这道难题。
九、结果状语从句
句型39、主句+so that+从句. 如:
It was very cold, so that the river froze.天气很冷,因此河水结冰了。
句型40、So+形容词/ 副词+特定动词+主语+…+that+从句.
So interesting is this book that I would like to read it again.这本书那么有趣,我想再读一遍。
句型41、主语+谓语+such+名词+that+从句.如:
He made such rapid progress that he was praised by the teacher.他进步很快,老师表扬了他。
句型42、Such was + 主语+that +从句.(这是个完全倒装句。)如:
Such was the force of the explosion that all the windows were broken.爆炸力这么大,所有的窗户都被震碎了。
十、比较状语从句
句型43、The +形容词比较级……,(主句)the +形容词比较级+……如:
The sooner you do it, the better it will be.越早越好。
句型44、主语+谓语+as +形容词原级+as +被比较的对象. 如:
He is as busy as a bee.他非常忙。
句型45、主语+谓语+the+形容词比较级+of / between …
He is the taller of the two.他们俩人中他高。
句型46、主语+谓语+倍数+as+形容词原级+as+被比较的对象.如:
This room is three times as large as that one.这个房间是那个房间的三倍大。(这个房间比那个房间大两倍。)
句型47、主语+谓语+百分数/倍数+形容词比较级+than+被比较的对象.如:
This city is twice larger than ours.这个城市比我们城市大两倍。
The early rice output in that commune was 200% more than that of 2000.那个公社的早稻产量是2000年的两倍。
句型48、主语+谓语+the size / length/ width/ height +of +被比较的对象.如:
Our building is twice the height of yours.我们的大楼比你们的高两倍。
十一、其它句型
句型49、It doesn’t matter wh-+从句。如:
It doesn’t matter to me what you will do tomorrow.你明天做什么与我无关。
It doesn’t matter whether you will come or not.你来不来无关紧要。
句型50、形容词/ 副词 / 名词(可数单数)+as / though +主语+谓语,+主句.如:
Young as he is, he knows a lot.虽然他很小,但他知道得很多。
Hard he works, I am sure that he can’t pass this exam.虽然他学习很努力,这次考试他肯定不能及格。
Child as he is, he knows a lot.虽然他是个孩子,但他懂得很多。
句型51、Were / Should / Had +主语+谓语,+主句.如
Were I you, I would he gone there yesterday.如果我是你的话,昨天我就去那儿了。
句型52、Only +状语+特定动词+主语+谓语…
Only by this means can I do this work well.只有用那种方式我才能做好此工作。
Only because he was ill did he not come to school.只因为他有病了才没有来上学。
Only then did I realize that I had been wrong.只有那时,我才认识到我错了。
句型53、Not only +特定动词+主语+谓语…but also+主语+谓语…
Not only did he learn English well but also he spoke French very well. 他不但英语学得好,而且法语讲得很流利。
句型54、whether….or…, neither…nor…, either…or…
句型55、主语+dou+whether + 从句. 请比较:
主语+特定否定词+dou+that+从句. 如:
I don’t dou that he will come this afternoon.我确信他下午一定能来。
十二.句型1:too +adj./adv.+to do
The boy is too young to go to school.这孩子太小不能上学。
句型2:adj./ad v.+enough to do
The girl is old enough to go to school.这女孩到了上学的年龄。
句型3:...in order to do
He stood up in order to see better.他站了起来,好看清楚些。
句型4:...he to do
You'll he to go home now.现在你得回家了。
句型5:There's no time to do this.
There's no time for me to play now.现在我没时间玩。
英语 7种 基本句型
一英语基本句型-1主系表结构/S (主)+ V(谓)(lv)( 系动词)+ P(表)
The cake tastes delicious.
二英语基本句型-2主谓结构/S(主)+ Vi(不及物动词)(谓)
本结构是由主语加不及物的谓语动词构成,常用来表示主语的动作.
如:The sun rises.Tom has already left.
主语可有修饰语-定语,谓语可有修饰语-状语.
如:1.The red sun rises in the east.
三英语基本句型-3主谓宾结构/S (主)+ Vt (及物动词)(谓)+ O(宾)
本结构是由主语+及物的谓语动词+宾语构成.宾语成分的多样化使得这一结构异常复杂.
如:1.Tom made a hole in the wall.
四英语基本句型4 双宾语结构/S (主)+VT(谓)+ InO(间接宾)+ DO(直接宾)
说明:此结构由“主语+及物谓语动词+间接宾语(人)+直接宾语(事物)”组成.
如:He brings me cookies every day.
但若要先说出直接宾语(事物),后说间接宾语(人),则要借助于介词to或for.
如:He brings cookies to me every day.
五英语基本句型5 复合宾语结构/S (主)+ VT(谓)+ O(宾)+ O C(宾补)
说明:此结构由“主语+及物的谓语动词+宾语+宾语补足语”构成.宾语与宾语补足语之间有逻辑上的主谓关系或主表关系,若无宾语补足语,则句意不够完整.可以用做宾补的有:名词,形容词,副词,介词短语,动词不定式,分词等.
如:The sun keeps us warm.
六英语基本句型6 There be 句型
说明:此句型是由“there+be+主语+状语”构成,用以表达存在关系可以称“……有……”.它其实是倒装的一种情况,主语位于谓语动词 be 之后,there 仅为引导词,并无实际语意.
此句型有时不用be动词,而用 live,stand,e,go,lie,remain,exist,arrive等.
如:There stands a hill in the middle of the park.
英语中简单句的五种基本句型
英语的基本句型主要有五种,它们是:
1、主语———动词———表语
2、主语———动词
3、主语———动词———宾语
4、主语———动词———宾语———宾语
5、主语———动词———宾语———补语
掌握好这些基本句型,就可以为灵活运用语言打下良好的基础.下面分别讲解这五种句型.
一、主语---动词----表语
在这一句型中,动词是系动词,划线部分为表语.
1.Mr.Brown is an engineer.(名词做表语)
2.Gradualy he became silent.(形容词做表语)
3.She remained standing for a hour.(现在分词做表语)
4.The question remained unsolved.(过去分词做表语)
5.The machine is out of order.(介词短语做表语)
6.The television was on.(副词做表语)
7.His plan is to keep the affair secret.(动词不定式做表语)
8.My job is repairing cars.(动名词做表语)
9.The question is what you want to do.(从句做表语,即:表语从句)
注意:在下面的句子中,形容词做表语,在表语的后面常常接不定式结构.
I'm hy to meet you.
They are willing to help.
We are determined to follow his example.
二、主语———动词
在这一句型中,动词为不及物动词及不及物的动词词组.在有的句子中,不及物动词可以有状语修饰.
1.The sun is rising.
2.I'll try.
3.Did you sleep well?(well做状语,修饰不及物动词sleep)
4.The engine broke down.
注意:在此句型中,有少数不及物动词表达被动含义,表达主语本身所具有的特性,不用被动语态.
1.The book sells wel.
2.The window won't shut.
3.The pen writes smoothly.
4.Cheese cuts easily.
三、主语———动词———宾语
在此句型中,动词为及物动词,划线部分为宾语.
1.Do you know these people(them)?(名词或代词做宾语)
2.I can't express myself in English.(反身代词做宾语)
3.He smiled a strange smile.(同源宾语)
4.We can't afford to pay such a price.(不定式做宾语)
5.Would you mind waiting a few minutes?(动名词做宾语)
6.I hope that I he said nothing to pain you.(从句做宾语,即:宾语从句)
注意:并不是所有的及物动词都可以接上述各种情况做宾语,不同的动词有不同的用法,所以,在学习动词时,一定要掌握其用法.
四、主语———动词———宾语———宾语
在此句型中,动词可以称作双宾语动词,在英语中,这样的动词并不多,在学习遇时,要牢记.后面的宾语为间接宾语和直接宾语,其中间接宾语在前,一般表人,直接宾语在后,一般表物.这类句型有三种情况.
第一种情况,间接宾语可以改为to引导的短语.
1.He handed me a letter.
He handed a letter to me.
2.She ge me her telephone number.
She ge her telephone number to me.
第二种情况,间接宾语可以改为for引导的短语.
3.She sang us a folk song.
She sang a folk for us.
4.She cooked us a delicious meal.
She cooked a delicious meal for us.
第三种情况,直接宾语可以由宾语从句充当.
5.Tell him I'm out.
6.Can you inform me where Miss Green lives?
五、主语———动词———宾语———宾语补足语
在此句型中的动词,叫做可以跟复合宾语的动词,在英语中,这样的动词也不多.后面的宾语补足语是说明宾语的情况的,宾语和宾语补足语一起被称做复合宾语.这个句式是英语中比较复杂的一个句式,因为复合宾语的构成内容较多.下面句子中划线部分为宾语补足语.
1.He found his new job boring.(形容词做宾补)
2.The called their daughter Mary.(名词做宾补)
3.This placed her in a very difficult position.(介词短语做宾补)
4.We went to here house but found her out.(副词做宾补)
5.What do you advise me to do?(不定式做宾补)
6.We thought him to be an honest man.(tobe做宾补)
7.He believed them to he discussed the problem.(不定式的完成式做宾补)
8.He believed her to be telling the truth.(不定式的进行式做宾补)
9.Did you notice him come in?(不带to的不定式做宾补)
10.I saw her chatting with Nancy.(现在分词做宾补)
11.He watched the piano carried upstairs.(过去分词做宾补)
注意:在这个结构中,可以出现用it做形式上的宾语,把真正的宾语放在宾语补足语的后面.在此结构中,宾语常常是动词不定式或宾语从句.
1.He felt it his duty to mention this to her.
分析:it是形式宾语,hisduty是宾语补足语,to mention this to her是真正的宾语.
2.I think it best that you should stay with us.
分析:it是形式宾语,best是宾语补足语,that you should stay with us是真正的宾语.
注意:
1.习惯用语的使用
在英语中,有很多动词习惯用语,在学习的过程中,要注意它们的使用,不必分析单独每个词的使用.
例:
We are short of money.(be short of中short做表语)
She is always making trouble for her friends.(trouble做make的宾语)
He has carried out our instructions to the letter.(our instructions做词组carry out的宾语)
We are waiting for the rain to stop.(wait for后面的the rain是宾语,to stop是宾语补足语)
2.在英语中,大多数动词既可以做及物动词又可以做不及物动词,而且还会有一些固定词组,因此一个动词可以用于几种句型.
例:ask
①Did you ask the price?(直接接名词做宾语)
②She asked them their names.(接双宾语)
③I asked James to buy some bread.(接宾语加不定式做宾语补足语)
④I asked to speak to Fred.(接不定式做宾语)
⑤Didn't you ask him in?(在此句中和副词in连用)
⑥He has asked for an interview with the President.(组成固定词组ask for)
3.There be句型是一种特殊的句子,真正的主语在后面,含义为“有…”
①谓语动词和主语保持一致:There is a television in the sitting room.
②有两个或更多的主语时,动词一般和最近的一个保持一致:There are two girls and a boy dancing in the hall.
③主语的后面有时有修饰语:There are a lot of difficulties facing us.There were many things to be done(此处也可以使用to do).
④谓语动词be可以有时态的变化:There will be a concert in the park tonight.There was little change in him.
⑤谓语也可以有不定式构成的复合谓语.
There used to be a cinema here.
There seems to be something the matter with her.
Is there going to be any activity tonight?
⑥there be句式变疑问句,把be提前;变翻译疑问句也要借助there.
Is there any hope of getting the job?
There is nothing wrong with your watch,is there?
⑦there be句型中也可以使用诸如:live,follow,come,stand,sit,exist等不及物动词:
Once upon a time,there lived a fisherman on the island.
There came a knock at the door.
At the top of the hill there stands an old temple.
⑧用于非谓语的情况下,有时用不定式的复合结构there to be或动名词的复合结构和独立主格结构there being:
You wouldn't want there to be another war.(不定式的复合结构)
The teacher was satisfied with there being no mistakes in his homework.(动名词的复合结构)
There being nothing else to do,we went home.(独立主格结构)
■巩固性练习
请判断下列句子的结构类型
1.He is running.
2.The loud voice from the upstairs made him angry.
3.The little boy is asking the teacher all kinds of questions.
4.She seemed angry.
5.My father bought me a beautiful present.
6.Why do you keep your eyes closed?
7.Will you tell us an exciting story?
8.We must keep our classroom tidy and clean.
9.I heard the baby crying in the sitting room.
10.Can you push the window open?
答案:
1.主语---动词
2.主语---动词---宾语---补语
3.主语---动词---宾语---宾语
4.主语---动词----表语
5.主语---动词---宾语---宾语
6.主语---动词---宾语---宾语
7.主语---动词---宾语---补语
8.主语---动词---宾语---补语
9.主语---动词---宾语---补语
10.主语---动词---宾语---补语
英语中的五大句型
五大几本句式:
主谓(谓语为不及物动词)
主谓宾(谓语为及物动词或不及物动词加介词)
主系表
主谓宾+宾补
主谓+间宾+直宾(主谓双宾)
具体如下:
一)主 + 系 + 表语
例:You are a baby
系动词:联系动词(Link Verb),作为系动词,它本身有词义,但不能单独用作谓语,后边必须跟表语(亦称补语),构成系表结构说明主语的状况、性质、特征等情况。说明:有些系动词又是实义动词,该动词表达实义时,有词义,可单独作谓语。例如:
He fell ill yesterday. 他昨天病了。(fell是系动词,后跟补足语,说明主语情况。)
He fell off the ladder. 他从上摔下来。fell是实义动词,单独作谓语。
1)be动词--用来表示主语状态。
例如:He is a teacher. 他是一名教师。(is与补足语一起说明主语的身份。)
2)持续系动词--用来表示主语继续或保持一种状况或态度。
主要有:keep, rest, remain, stay, lie, stand。
例如:This matter rests a mystery. 此事仍是一个谜。
3)表像系动词--用来表示"看起来像"这一概念,
主要有:seem, ear, look。
例1: He seems (to be) very sad. 他看起来很伤心。
例2:—You don’t look very _____.Are you ill? ( 2003春)
—No, I’m just a bit tired.
A.good B.well C.strong D.healthy
句意:你看上去不是很健康,生病了吗?
答案:B
分析:look well 此时well是形容词表示健康
4)感官系动词
感官系动词主要有feel, smell, sound, taste。
例1:-Do you like the material? (1994)
-Yes, it __________ very soft.
A. is feeling B. felt C. feels D. is felt
句意:你喜欢这个材料吗?是的手感很软
答案:C
分析:soft形容词做feel的表语.感官系动词表示感觉所以要用一般现在时
例2:The story sounds___ (1989)
A. to be true B. as true C. being true D. true
句意:这个故事听起来是真的
答案:D
分析:sound是.感官系动词所以后加形容词做表语
例3: These oranges taste __________.
A. good B. well C. to be good D. to be well
句意:这些橘子吃起很好吃
答案:A
分析:taste是.感官系动词所以后加形容词做表语所以答案是A
5)变化系动词---这些系动词表示主语变成什么样,变化系动词
主要有:become, grow, turn, get, go 等。
例: It worried her a bit that her hair was turning gray.(1992)他头发变得灰白让他忧虑。
6)终止系动词--表示主语已终止动作.
主要有:prove, turn out, 表达"证实","变成"之意。
例:The rumor proved false. 这谣言证实有。
The search proved difficult. 搜查证实很难。
His plan turned out a success. 他的终于成功了。(turn out表终止性结果)
二) 主语+不及物动词 S + Vi
例:you are crying
三) 主语 + 谓语 + 宾语(及物,最少带1,最多带2)
例:I love you
四) 主+及物动词+宾语1+宾语2
例:I will give you a kiss.
可以带双宾语的动词:
买卖关系: buy pay cost
给予关系: give grant pass offer bring send
借还关系: lend return owe wish
说服关系: tell persuade
命名选举关系:name call elect select
其他关系:wish envy make
例1:We ______ each other the best of luck in the examination.(1991)
A. hoped B. wanted C. expected D. wished
句意:我们彼此祝愿考试
答案:D
分析:each other the best of luck两个都是宾语,能接双宾语的词只有wish
例2:I was wondering if you could tell me how to fill out this form (2002北京)我在想你是否能告诉我如何填这个表。
五) 主语+ 谓语 + 宾语 + 宾补(补充说明宾语状态)
例1:I will make you hy 我会使你快乐的。
高中英语五种基本句型及拓展
英语的句子在结构上可以归纳为五个基本句型。A.第一基本句型 例译1.正在下着雨。2.我的哥哥很用功。3.我每天早晨六点钟起床。4.日出于东而没于西。5.比尔和吉姆每天都一起读书一起玩。解说各例句的黑体字是主语,斜体字是谓语动词。主语通常是一个,但是也可以如例5有两个,甚至两个以上都可以成立。谓语动词也是一个较为普通,但是也可以如例4,5有两上,甚至更多也能成立。本句型的Vi.属于完全不及物动词(Complete intransitive verb).注:“There + be(Vi. ) + S…”也是属于第一基本句型。例如:例:There is an alarm clock on her desk.(她的书桌上有一个闹钟。)例:There stands a tower on the hill.(小山上耸立着一座塔。) B.第二基本句型 例译1.我的名字是汤姆。2.约翰和玛丽是同班同学。3.你准备好了吗?4.所有的问题都不容易回答。5.你的梦想一定能实现的。6.这些玫瑰花看起来很美,闻起来也很香。解说各例句的黑体字是主语,斜体字是谓语动词,字底加线的是主语补语。什么是主语补语?请观察:①My name is(我的名字是)②These roses look(这些玫瑰花看起来)上面两例虽各有可作主语的名词“name”和“roses”,也有谓语动词“is”和“look”,但是句意不清楚,无法表达完整的句意,所以不是句子。现在若在例1之后加“Tom”,例2之后加“very beautiful”,那么句意就完整地表达出来了。像这样,一个词(通常是n.pron.或adj.)在谓语部分里补充说明主语者就叫做主语补语。主语补语通常是一个,但是依表达的需要也可以有两个(如例6),或更多。谓语动词需要取主语补语才能把句意表达完整者叫做不完全不及物动词(Incomplete intransitive verb)。注:下列常见“It…”句式也是属于第二基本句型。1.It + be + a/n .+ to v…(不定式)例:It is nice to see you again.(能再和你见面真好。)例:It is your duty to take care of your mother.(照顾你的妈妈是你的责任。)2.It + be +adj +for +o + to V…例:It is easy for us to learn to speak English.(学习说英语对我们来说是容易的。) C.第三基本句型
例译1.现在我们正在学习句型。2.海伦做她的课外作业都很小心。3.昨天你看到他了吗?4.我们的英语老师林先生会说英语和日语。5.大部分的小孩都爱阅读故事。解说各例句的黑体字是主语,斜体字是谓语动词,字底加线的是直接宾语。直接宾语(请参阅L-3,第3节,D,注)通常以名词、代词(宾格)为多,其他如不定式、动名词(如例5)、或名词从句等也可用。直接宾语也可以取两个(如例4),或两个以上。谓语动词取了直接宾语就能表达完整的句意者叫做完全及物动词(Complete transitive verb)。 D.第四基本句型 例译1.她的伯父昨天给了她一件很好的礼物。2.请给我们一些吃的东西。3.这位老师常给这些男、女生讲有趣的故事。4.她的父亲上星期买了一只新的手表给他。5.我的美国朋友比尔在几天前写了一封信给我。解说本句型的谓语动词所发出的动作有两个对象,一为“人或动物等”,称为间接宾语,另一为“物或事”,称为直接宾语。本句型也可以把“D.O.”置于“I.O.”之前表达如下:Her uncle ge a nice present to HER yesterday.His father bought a new watch for HIM last week.如上例所示,本句型即变为: 至此我们可以明白,间接宾语实际上是介词的宾语,不过因为它间接地也是谓语动词所发出的动作的对象,所以称为间接宾语。取间接宾语和直接宾语的谓语动词叫做授与动词(Dative verb)。本句式在语序上以“I.O.+D.O.”较普通,尤其是“I.O.”为简短的一个名词或代词时,无论是对话或文体,通常都使用“I.O.+D.O.”。所以通常应该说:Give the BOY something to eat.(给那男孩吃的东西。)Make ME a cup of hot coffee, please.(请泡一杯热咖啡给我。)而避免说:Give something to eat to the BOY.Make a cup of hot coffee for ME, please.“I.O.”置于“D.O.”之后时,介词或用“to”,或用“for”,通常都是由Vt.来决定,因此在学习过程中请随时注意。 E.第五基本句型 例译1.他们都叫他“小胖”。2.他使他的年老的母亲很快乐。3.老师经常都要我们坐得端正。4.你有办法发动这部汽车吗?解说本句型的“O.C.”是宾语补语。那么什么是宾语补语?请观察例2如下的说明:He made his old mother(他使得他的年老的母亲)这个词群虽有主语、谓语动词和宾语,完全符合第三基本句型的条件,可是这个词群并没有表达完整的句意,所以不是句子。如果在这个词群的宾语之后再加“very HAPPY”(如例2),那么句意就完整清楚了。在这句里谁是“very HAPPY”?“He”or“mother”?当然是“mother”。因此:定义 置于宾语之后补充说明宾语者叫做宾语补语(Object Complement)。谓语动词需取宾语补语才能完整清楚地表达其句意者称为不完全及物动词(Incomplete transitive verb)。注:1.一般的英语词典对动词的标示只作“Vi.”或“Vt.”两种,至于“完全Vi.”,或“不完全Vi.”;“完全Vt.”或“不完全Vt.”则须自行判断了解。2.绝大多数的动词都可以作“Vi.”或“Vt.”使用,但是所表达的语义却不相同。例如:例:He can run very fast.(他能跑得很快。—“run”是“Vi.”)He runs a department store in Beijing.(他在北京经营一家百货商店。—“run”是Vt.)又同是“Vi.”,或同是“Vt.”,因其为“完全”或“不完全”也有不相同的语义。例如:例:He believes that God is.(他相信上帝存在。—“is”是完全“Vi.”)He is a Christian.(他是一个基督教徒。—“is”是不完全“Vi.”)例:Can you make cakes?(你会做蛋糕吗?—“make”是完全“Vt.”)Our teacher sometimes makes us do our homework.(我们的老师有时候会强迫我们做课外作业。—“make”是不完全的“Vt.”)3.由五个基本句型的解释我们可以了解,决定英语句子型式的要素是谓语动词,因此我们若要学好英语,必须对英语动词的表达功能有正确的认识和了解。Drilling Square Vt.Ⅰ.请判断下列各句各属于哪一个基本句型。1.Do you know her younger sister?2.I got home after dark yesterday.3.Bill always does very well at school.4.What pet do you keep?5.There were some students reading in the classroom then.6.Amy always helps her mother after school.7.Tom often makes his teacher angry.8.Did you see anyone go into that house?9.Helen looks very hy today.10.I was born in a little town in the south of Taiwan.Ⅱ.请阅读下列短文,然后判断底部加线的句子各属于哪一基本句型。①One summer evening Newton[>nju:tn](牛顿)sat quietly on a bench in the garden. ②An le fell to the ground from a tree. He saw it and thought: ③ “Why did an le fall?”④He studied very hard.⑤ Later he found out the reason.⑥One day Newton sat at his desk.⑦ He was studying very hard. His servant came into the room. ⑧ He left an egg on his desk.⑨ There was a watch on the desk.⑩ Into the boiling water in the kettle Newton put the watch instead of the egg.
英语5个基本句型例句
一、主语+系动词(be)+表语句型;
二、主语+谓语动词(不及物动词);
三、主语+动词(及物动词)+宾语;
四、主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语;
五、主语+谓语+宾语+状语。
扩展资料
第一种句型是:主语+系动词(be)+表语句型。
在这类句型中,谓语动词是系动词(be)的形式,主要有is、am、are、was、were。
比如:I am a student and very like English class.
我是一个学生非常喜欢英语课。
He is the frist in my class.
他是我们班第一名。
These les are very fresh, you need eat it every day.
这些苹果非常新鲜,你必须每天吃一个。
第二种句型是:主语+谓语动词(不及物动词)。
在这类句型中,谓语动词是不及物动词,这类动词后面是不可以接宾语的,但是可以接任意性状语。所谓的任意性状语是指去掉后,并不会影响句子完整的结构和意义。
比如:The orange was not to keep for a long time.
橘子是不好长期保存的。
He had left here yesterday.
他昨天已经离开了。
I can’t sleep in the night.
我晚上失眠了。
第三种句型是:主语+动词(及物动词)+宾语。
在这类句型中,谓语动词是及物动词,而且是只接一个宾语的及物动词,这种动词我们经常称为单宾语及物动词。
比如:He had left my home yesterday , he can’t tell you.
他昨天已经离开我家了,他没有告诉你。
She ate the dinner with her mother.
她和她妈妈一起吃的.晚饭。
I has left the Beijing by the train.
我乘坐火车离开了北京。
第四种句型是:主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语。
在这类句型中,谓语动词是能够接两个宾语的及物动词,我们经常称这类动词为双宾语动词。比如:She give me a new book in my birthday.
在我生日上她送给了我一本新书。
Shall I lee you the dictionary ?
要我把这本字典留给你吗?
I ge you a le as a gift in our first meet.
我用一个苹果作为我们第一次见面的礼物。
第五种句型:主语+谓语+宾语+状语。
比如:I he left Beijing at five.
我在五点就离开了北京。
He often played basketball at afternoon.
他经常在下午打篮球。
She like listen to music.
她喜欢听音乐。
用英语的五种基本句型造各造5个句子
1、主语+谓语,如:we agree.
2、主语+谓语+宾语,如:I hate him、I love you.
3、主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语,如:I give him a book.
4、主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语,如:I want you to go with me.
5、主语+系动词+表语,如:It smells good.
扩展资料
句型1: Subject (主语) + Verb (谓语):
这种句型中的动词大多是不及物动词,所谓不及物动词,就是这种动词后不可以直接接宾语。
1) Li Ming works very hard.李明学习很努力。
2) The accident hened yesterday afternoon.事故是昨天下午发生的。
句型2:Subject (主语) + Link. V(系动词) + Predicate(表语)
这种句型主要用来表示主语的特点、身份等。其系动词一般可分为下列两类:
(1)表示状态。这样的词有:be, look, seem, smell, taste, sound, keep等。如:
This kind of food tastes delicious.这种食物吃起来很可口。
(2)表示变化。这类系动词有:become, turn, get, grow, go等。如:
Spring comes. It is getting warmer and warmer.春天到了,天气变得越来越暖和。
句型3:Subject(主语) + Verb (谓语) + Object (宾语)
这种句型中的动词一般为及物动词, 所谓及物动词,就是这种动词后可以直接接宾语,其宾语通常由名词、代词、动词不定式、动名词或从句等来充当。
例:
1) He took his bag and left.(名词)他拿着书包离开了。
2) Li Lei always helps me when I he difficulties. (代词)当我遇到困难时,李雷总能给我帮助。
3) I don’t know what I should do next. (从句)我不知道下一步该干什么。
注意:英语中的许多动词既是及物动词,又是不及物动词。
四、句型4: Subject(主语)+Verb(谓语)+ Indirect object(间接宾语)+Direct object (直接宾语)
这种句型中,直接宾语为主要宾语,表示动作是对谁做的'或为谁做的,在句中不可或缺,常常由表示“物”的名词来充当;间接宾语也被称之为第二宾语,去掉之后,对整个句子的影响不大,多由指“人”的名词或代词承担。引导这类双宾语的常见动词有:buy, pass, lend, give, tell, teach, show, bring, send等。如:
1) Her father bought her a dictionary as a birthday present.她爸爸给她买了一本词典作为生日礼物。
2)The old man always tells the children stories about the heroes in the Long March.
老人经常给孩子们讲述长征途中那些英雄的故事。上述句子还可以表达为:
1)Her father bought a dictionary for her as a birthday present.
2)The old man always tells stories about the heroes to the children in the Long March.
五、句型5: Subject(主语)+Verb (动词)+Object (宾语)+Complement(补语)
这种句型中的“宾语 + 补语”统称为“复合宾语”。宾语补足语的主要作用或者是补充、说明宾语的特点、身份等;或者表示让宾语去完成的动作等。担任补语的常常是名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、分词、动词不定式等。如:
1)You should keep the room clean and tidy. 你应该让屋子保持干净整洁。(形容词)
2) We made him our monitor.(名词)我们选他当班长。
3) His father told him not to play in the street.(不定式)他父亲告诉他不要在街上玩。
五种基本句型:
1、“主语+谓语”(即“主谓”句型)
They worked day and night.
2、“主语+谓语+宾语“(即”主谓宾“句型)
He raised his arms.
3、“主语+系动词+表语“(即”主系表“句型)
I am a teacher.
4、”主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语“(即”主谓双宾“句型)
Miss Zhang ge us an English lesson.
Miss Zhang ge an English lesson to us.
5、”主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语“(即”主谓宾宾补“句型)
I heard her singing in the next room this time yesterday.
声明:本站所有文章资源内容,如无特殊说明或标注,均为采集网络资源。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。












