怎么看英语句子的结构_怎么看懂英语句子结构
1.怎么分析英语句子的结构,主语,等等之类的啊?
2.英语语法,有时候分不清主谓结构和不完整句,有主谓了却还缺个宾语,应该怎么看是完整句还是不完整句?
3.怎样分析一个英语句子的结构
4.英语句子的组成部分的解析
5.英语题目如何分析句子结构
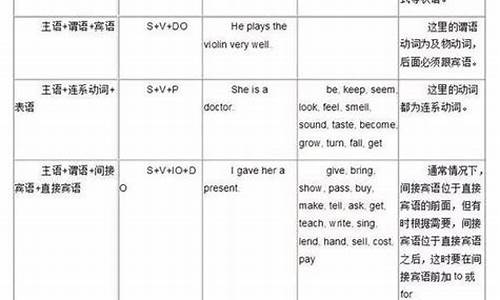
1主语就是发起动作的人或物,由名词,名词性短语或代词构成
2谓语就是动作,动词或动词短语
3宾语就是承受动作的人或物,由名词,名词性短语或代词构成
4定语就是修饰句中名词的成分,可以是形容词做定语,也可以是定语从句
5状语就是修饰谓语动词的,例如说明动作是说明时候发生的,就是时间状语;动作是怎样发生的就是方式状语,还有地点状语等,由副词构成,以及9种状语从句
6补语就是做补充说明成分的,补充说明主语的是主语补语,补充说明宾语的是宾语补语
The pretty girl sings songs on the stage every Sunday.
4 1 2 3 ( 5 )( 5 )
English drives me mad.
1 2 3 6
希望能帮到你!
怎么分析英语句子的结构,主语,等等之类的啊?
英语中有五大句子结构:
1)主系表结构(主语+联系动词,也叫 Be 动词+表语),例如:I am a student(我是个学生).
2)主谓结构(主语+谓语),例如:I work(我工作) I sleep(我睡觉).
3)主谓宾结构(主语+谓语+宾语),例如:I study English(我学习英语).
4)主谓双宾结构:(主语+谓语+2个宾语),例如:She ge me an le.(给我一个苹
果),其中 She 是主语,ge 是谓语,me 和 le 都是宾语,所以称作双宾语。双宾语可
以转换成:She ge an le to me.
5)主谓宾加宾补结构:(主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语),例如:I see a girl dancing.(我看见
一个女孩在跳舞),dancing(跳舞)是动名词做宾语补足与,与宾语有主谓关系。
英语语法,有时候分不清主谓结构和不完整句,有主谓了却还缺个宾语,应该怎么看是完整句还是不完整句?
一个句子一般由两部分构成,即主语部分和谓语部分,这两部分也叫做句子的主要成分。句子的次要成分包括宾语,定语,状语,表语等。
主语:是一句的主体,是全句述说的对象,常用名词,数词或代词担任,一般放于句首。
谓语:是对主语加以陈述,表示主语的行为或状态,常用动词或者动词词组担任,放在主语的后面。最常见的就是be动词。
宾语:表示行为的对象,常由名词或者代词担任。放在及物动词或者介词之后。
定语:是用来说明或者限制名词的成分,常用形容词或者相当于形容词的短语或从句担任。形容词放在名词之前,相当于形容词的短语或从句放在名词的后面
状语:是用来说明动词,形容词,副词或整个句子的成分。常由副词担任。修饰动词时可以放在动词之前,也可以放在动词之后;修饰形容词或副词时放在它们之前。
表语:用来说明主语的性质或状态。一般由名词或者形容词担任。
怎样分析一个英语句子的结构
看是完整句还是不完整句,就要认识句子的成分结构,总结如下:
一、 简单句
1.主语+谓语(不及物动词)
2.主语+谓语+宾语
3.主语+ 系动词+表语
4.主语+谓语+双宾语
5.主语+谓语+宾语+ 宾补
二、并列句是两个或以上的简单句使用并列连词and /but /or /so/for 连接
三、两个简单句,其中之一使用了从属连词,就是从句.另一个就是主句.
简单句的五种基本结构是句子的基础.
英语句子的组成部分的解析
答:你首先要知道英语的句子成份有七种 :主、谓、宾、定、状、补、表。
其次知道按结构分,句子有三种:简单句、并列句和复合句。
你要知道五种基本的简单句句型:
主系表
主谓
主谓宾
主谓宾宾
主谓宾补。
接下来要知道十大词类在句子中的作用。比如名词常作主语、宾语、表语等等。更要知道动词的种类,有系动词(be动词等等),不及物动词、及物动词。及物动词又有三类。
总之,先要掌握基本的句法知识,才能进行句子结构分析。要展开就是语法书了。
英语题目如何分析句子结构
Different parts of a sentence概念句子是由词按照一定的语法结构组成的.组成句子的各个部分叫做句子的成分.句子的成分包括:主语、谓语、表语、宾语(直接和间接宾语)、宾语补足语、定语和状语.主语和谓语是句子的主体部分(在英语中,一般句子必须有主语和谓语),表语、宾语和宾语的补足语是谓语里的组成部分.其他成份如定语和状语是句子的次要成分.▲句子成分分类1.主语 主语是谓语讲述的对象,表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”.一般由名词、代词、不定代词或相当于名词的单词或短语来充当,也有从句充当的现象.大多数主语都在句首.如:讲述“谁”We work in a big factory. 讲述“什么”The classroom is very big. 数词作主语Three are enough. 三个人就够了不定式作主语To operate on the blind is one of the ORBIS Doctor’s job.从句作主语What we need is food. 我们最需要的是食物.▲ 在“There be …”句型中,主语的位置在中间.如:There are some bottles of milk in the box.▲ 在个别句型中,主语在整个句子后面,这时前面用it作形式主语.如: It is very interesting to play the game called “treat or trick”. It took two workers about three months to build the house.2.谓语谓语时用来说明主语“做什么”、“是什么”或“怎么样”,谓语必须是动词,谓语和主语在“人称”和“数”两方面必须一致.如:He is very generous.She looks very smart and coolWe he finished the job.He can speak German.3.表语 表语说明主语“是什么”或“怎么样”,由名词、形容词、介词、副词、不定式及相当于名词的词或短语来充当,它的位置在系动词后面. 形容词作表语You look younger than before. 名词作表语 My father is a teacher. 副词作表语Everyone is here.介词短语作表语They are at the theatre.不定式作表语My job is to teach them English.动名词作表语Her job is training the nurses.从句作表语That is why he didn’t come to school yesterday.4.宾语▲宾语是动作、行为的对象,由名词、代词、不定式、或相当于名词的词或短语或从句来充当,它和谓语动词一起说明主语是什么,通常放在谓语动词后面.有时,会有双宾语.如:名词作宾语He never forgives others for their mistakes.代词做宾语He often helps me.不定式作宾语He likes to sleep in the open air.动名词作宾语The Americans enjoyed living in China.从句做宾语I believe that they can finish the work in time.▲直接宾语和间接宾语及物动词作谓语时,后面要跟宾语,宾语分直接宾语和间接宾语.直接宾语是及物动词的对象.但有些动词除了直接宾语外,还需要有一个间接宾语,间接宾语表语动作是对谁做的,所以只能用名词或代词来充当.如:We brought them some food.主 谓 间宾 直宾间接宾语可以放在直接宾语后面,但必须加to 或 for.5.宾语的补足语 在英语的句子中有些句子里只有宾语并不能表达完整的意思,还必须在宾语后面加上宾语的补足语才能表达完整的意思.我们把“宾语+宾语补足语”合起来称为复合宾语.复合宾语所表达的意思相当于一个巨资的意思.名词、动词、形容词、副词、介词短语、不定式、现在分词、过去分词都可以作宾语补足语.如:名词作宾补If you let me go, I’ll make you king.形容词作宾补Don’t make your hands dirty.副词作宾补We found Li Ming out when we arrived.介词短语作宾补Make yourself at home.省略to的不定式作宾补I saw a girl go into the building.带to的不定式作宾补The boy ordered the dog to lie down.现在分词作宾补The boss kept them working all day.过去分词作宾补Yesterday he got his leg broken.在英语中,常见的“宾语+宾语补足语”的结构有:▲“宾语+名词”.常用于改结构的动词有:call, name, make, find, choose, think, lee等. We call him Jack. They made Li Lei their monitor.▲“宾语+形容词”.常见的动词有think, believe, lee, drive, make, keep, turn, wish, want等.如:Do you think his idea wrong?We must keep our classroom clean.We can’t lee him alone.Can you get everything ready for the party before Friday?▲“宾语+副词”.副词作宾补常表示宾语的状态,与宾语有逻辑上的主表关系.常见的副词有:down, up, here, there, home, in, out, anywhere等.如: Let him in/ out. Mr. Li drove us home.When got there, we found him out.▲“宾语+介词短语”.介词短语作宾补常表示其逻辑主语(即宾语)所处的状态,两者有主表的关系.如: We found everything in good order. We regard him as our good friend.He opened the door and found some of his friends in the rain.▲“宾语+不定式”.充当宾补的不定式有三种: A 要求带to的不定式The cool water of the lake invited us to swim. B 要求不带to 的不定式 let, make, see, hear, watch等 The boss made the workers work 12 hours a day. I often hear him read English in his room. C 单词help 后可加 to 或不加 to She sometimes helps her mother (to) do housework.▲“宾语+现在分词”.现在分词作宾补,此时在该句型中的宾语即为现在分词逻辑上的主语,有着主谓关系. I saw them playing on the playground.I heard Mary singing in the classroom.▲“宾语+过去分词”.宾语和宾补之间是被动关系,过去分词表示被动和完成. I had my bike stolen. The teacher explained again and again to make himself understood.▲ 形式宾语+形容词 We found it impossible to get there before Saturday.▲宾语+what 从句Call me what you like.Mr. Li has made the factory what it is today.The mountain village is different from what it was ten years ago.6.定语▲ 定语用来修饰名词或代词.形容词、代词、数词、名词、介词短语、不定式或相当于形容词的词或短语等都可以充当定语.因为它是修饰名词或代词的,而名词和代词可以作主语、表语或宾语,所以定语的位置很灵活,凡是有名词、代词的地方都可以有定语.如: 形容词作定语 The black bike is mine. 代词作定语 What’s your name?名词作定语They made some paper flowers.介词短语作定语 The boys in the room are in Class Three, Grade One.不定式作短语 I he lots to eat and drink.从句作定语 The tall boy who is standing there is Peter.▲ 在英语中,并不是所有的定语都放在被修饰词的前面,有的是放在被修饰词的后面,故称“后置定语”.▲ 修饰不定代词 something, anything, nothing, something, anyone, somebody, anybody, nobody 的定语必须后置.如: We’ll go to he something English. If you don’t know the answer, ask someone else. Do you he anything important to tell me?▲介词短语作定语时要后置.如: Do you know the boy behind the tree?
The students in the room are all my friends. I think the picture on the left is better than the one on the right.▲动词的不定式作定语时要后置 What about something to drink? I he no time to trel to China is in Autumn or in Spring.注 动词不定式作主语时,to 后面的动词必须是及物动词或相当于及物动词的短语.如果时短语时,那么与动词搭配的介词或副词是不能少的. Do you he any piece of music to listen to? ▲nearby, below, downstairs等个别方位词作定语时要后置.如:We are at the top of the hill. Can you see the village below?The people downstairs are listening to a talk now?They took the boy to the hospital nearby at once.7.状语 状语用来修饰动词、形容词或副词.它表示行为发生的时间、地点、目的、方式、程度等,一般由副词、介词短语、不定式,从句或相当于副词的词或短语来充当.状语一般放在句末,但有时也可以放在句首、句中.如: He did it carefully They missed me very much. Without his help, we couldn’t work it out. In order to catch up with my classmates, I must study hard. When I was young, I could swim well.
1、简单句
英语的简单句只有五种基本句型,所有的英语句子都不能离开这五种基本句型,所以我们把它们谙熟于心是非常重要而且大有裨益的。这五种句型是:SV , SVC , SVO , SVOC , SVOiOd。其中S = Subject,也就是主语;V = Verbal phrase,也就是谓语部分;C = Complement ,表示跟在系动词之后的补语;O = Object,也就是句子的宾语,在最后一种句型中包括间接宾语和直接宾语。这五种句型的形成依靠的是谓语部分的动词的用法,动词的用法又是和它的意义不可分的。比如hit这个词,它的意思是挚骁,那么挚骁这个动作必须有一个执行者,就是主语。同时它还少不了一个受事者,也就是宾语,不然就产生不了完整的意义。而smile就不同了,它可以只有一个主语,而没有宾语。从这些简单的例子中我们可以看出谓语部分在句子中的极端重要性。我们在阅读句子的时候,第一个任务就是要找到谓语在什么地方。
2、并列句(compound sentence)
英语的并列句一般情况下引不起巨大的阅读障碍,因为在分句之间往往有固定的连接词说明前后分句的关系。这样的连接词有以and为代表的表示意义延伸的并列连词、以or为代表的表示选择概念的并列连词、以but为代表的表示转折的并列连词和表示原因的for四个类型。第一种包括and, not only … but (also )…, neither ( nor) 。第二种包括or , either … or …;第三种包括but , while , whereas等。第四种只有一个for。对此我们分别举一个例句说明问题:
(1)As is reported, a trade agreement was signed and a cultural exchange was arranged.
(2)Not only is he himself interested in the subject but all his students are beginning to show an interest in it.
(3)Dr. Fisher neither loves the environment, nor is he accustomed to the weather.
(4)The children can go with us , or they can stay at home.
(5)You can either go it by yourself, or you can ask someone else to do it.
(6)The young man has often been praised , but he is never conceited.
(7)While our country has plenty of oil , theirs has none.
(8)They want to live in town , whereas we would rather live in the country.
(9)They arently he a good drainage system , for the streets never seem to flood after a downpour.
3、 从属句
构成从属关系的复杂句包括名词性分句(Nominal Clauses)(可以作主语、宾语、同位语、主语补语)、关系分句(Relative Clauses)、状语分句(Adverbial Clauses)。对于它们的连接词,在相应的语法书上都不难找到,这里就不再多讲了。需要提醒读者的是,在判定句子的类型之后,最主要的工作就是分析简单句的成分,找到主句的谓语,真正抓住句子的纲领。下面请作练习二,首先辨认多重分句的类型,然后找出主句和从属分句的谓语。
Laboratory scientists accustomed to noticing sule changes in the properties of substances they are investigating are douless better than you or I at certain sorts of observations.
这里的主语是Laboratory scientists,但是后面跟了一个过去分词定语,其中分词中的介词又跟了一个-ing形式,-ing形式后又接了一个宾语和一个带有定语的状语。本句的谓语是are douless better than。
声明:本站所有文章资源内容,如无特殊说明或标注,均为采集网络资源。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。












